Yes, because if we build enough of them they'll suck up all the heat from the sun's rays. However, they would also suck up all the light. And because it would be so dark and cold, people would need their heating and lights on at all times, so the energy consumption actually would go up. My chiropractor calls it "The Solar Panel Paradox".
No Stupid Questions
No such thing. Ask away!
!nostupidquestions is a community dedicated to being helpful and answering each others' questions on various topics.
The rules for posting and commenting, besides the rules defined here for lemmy.world, are as follows:
Rules (interactive)
Rule 1- All posts must be legitimate questions. All post titles must include a question.
All posts must be legitimate questions, and all post titles must include a question. Questions that are joke or trolling questions, memes, song lyrics as title, etc. are not allowed here. See Rule 6 for all exceptions.
Rule 2- Your question subject cannot be illegal or NSFW material.
Your question subject cannot be illegal or NSFW material. You will be warned first, banned second.
Rule 3- Do not seek mental, medical and professional help here.
Do not seek mental, medical and professional help here. Breaking this rule will not get you or your post removed, but it will put you at risk, and possibly in danger.
Rule 4- No self promotion or upvote-farming of any kind.
That's it.
Rule 5- No baiting or sealioning or promoting an agenda.
Questions which, instead of being of an innocuous nature, are specifically intended (based on reports and in the opinion of our crack moderation team) to bait users into ideological wars on charged political topics will be removed and the authors warned - or banned - depending on severity.
Rule 6- Regarding META posts and joke questions.
Provided it is about the community itself, you may post non-question posts using the [META] tag on your post title.
On fridays, you are allowed to post meme and troll questions, on the condition that it's in text format only, and conforms with our other rules. These posts MUST include the [NSQ Friday] tag in their title.
If you post a serious question on friday and are looking only for legitimate answers, then please include the [Serious] tag on your post. Irrelevant replies will then be removed by moderators.
Rule 7- You can't intentionally annoy, mock, or harass other members.
If you intentionally annoy, mock, harass, or discriminate against any individual member, you will be removed.
Likewise, if you are a member, sympathiser or a resemblant of a movement that is known to largely hate, mock, discriminate against, and/or want to take lives of a group of people, and you were provably vocal about your hate, then you will be banned on sight.
Rule 8- All comments should try to stay relevant to their parent content.
Rule 9- Reposts from other platforms are not allowed.
Let everyone have their own content.
Rule 10- Majority of bots aren't allowed to participate here.
Credits
Our breathtaking icon was bestowed upon us by @Cevilia!
The greatest banner of all time: by @TheOneWithTheHair!
Your Chiropractor sounds like they’re equally credentialed in thermodynamics as they are in medicine.
He cricks my neck real good so he must know a thing or two
Technically, if you built enough solar panels in space, they would completely block the sun and massively decrease global temperature
Conservation of energy equation says otherwise.
Elaborate?
Yes. If we built a giant circle of solar panels in space around the sun, it would cool the earth to the point it would be unliveable for humans.
No. If a watt worth of sunlight hits the earth, it's transformed into a watt of heat. If it hits a solar panel, it's transformed into some heat and some electricity, which is then used to power something that then transformed it into heat. The only solar energy that doesn't heat up the planet is the one that is reflected back into space, which, however, isn't much for solar panels.
However, if you use a watt of sunlight to power your phone instead of a watt of energy you got from burning coal, this watt of energy instead stays below earth and therefore doesn't heat up the planet. It also doesn't release co2, which would otherwise reduce the atmosphere's reflectivity, trapping even more sun heat on the planet.
So solar panels don't reduce the temperature by not allowing sunlight to heat up the planet, they decrease the temperature by replacing other stuff that would otherwise heat up the planet.
Solar panels aren’t 100% efficient though, so isn’t a bunch of it is reflected back in to space?
Isnt the energy also stored in batteries until ready to be used?
Yeah, so what? Eventually, it'll be heat.
co2, which would otherwise reduce the atmosphere’s reflectivity
Just to be pedantic CO2 absorbs bands in the infrared and reemits it, energy that otherwise could be lost to space. This is part of the reason you can't do infrared telescopes from earth.
https://news.climate.columbia.edu/2021/02/25/carbon-dioxide-cause-global-warming/
Water is an even more powerful greenhouse gas but fortunately the earth is cool enough for it to condense back out of the atmosphere. If temps got high enough that more evaporated than condensed then you'd get a runaway greenhouse effect and we'd be truly fucked.
Your comment in pictures:
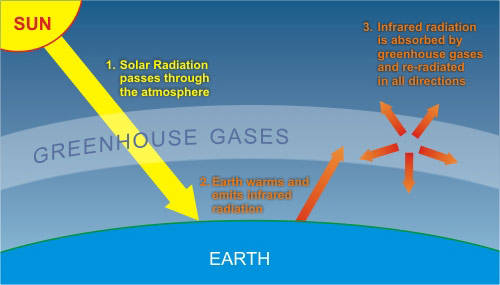
Just note that the released energy of burning fossils (or nuclear) is orders of magnitude below what the sun does. It really is only the CO2 from coal (or CO2 and CH4 from natural gas, ...) that does the heating, since it acts like insulation.
Yeah, that explanation sounded off to me. CO2 and other greenhouse gases are the issue, not heat directly released from combustion. The sun is doing the overwhelming majority of heating. Carbon staying underground matters far more than watts staying underground.
Plants fixing carbon also converts energy to a form that isn’t heat, so I think we should count that along with reflection as a way that solar energy doesn’t become terrestrial heat.
Correct, but not only is it extremely little, this stored energy is also quickly released again after the organism dies.
quickly
Quick in geologic time. But this is what fossil fuels are, so it’s an order of magnitude or two different than the time in which generated electricity will be used.
And you’re right, it’s very small. Everything we know is pretty small, even combined. The amount of energy the sun imparts to the Earth every day equals what humanity would use over about 12 years at current levels.
No, quickly as in years. There is no more coal or oil formed today, there are now organisms that can digest every part of organic stuff. There were none back then for example for lignin from wood, which is where we got coal from.
Not directly. That electricity is converted to heat when it's used: All devices are space heaters, some just do other things as well. Even if not used, it would still be converted to heat by the panels. There's no getting around the conservation of energy.
In theory, we could send that power out into space as microwaves or light, but in practice the effect would be negligible. The direct heat output of every human activity is nothing compared to the sun: All the electricity generated on earth is around 3 Terrawatts, while the sun hits us with 200 Pettawatts, 66 thousand times more.
On the other hand, burning fuels releases gasses like CO2, which can traps sunlight and creates thousands of times more heat than the actual amount of power generated. If we stopped burning fuel, it would stop the current massive increase in global temperature, which would then slowly be reversed by things like the carbonate-silicate cycle.
That electricity is converted to heat when it’s used
a missing point is that fossil fuels use 3-4 watts of heat to make 1 watt of electricity or mechanical movement. Electric heat pumps can sometimes make 3-4 watts of useful enough (home) heat from 1 watt of electricity.
but not all of it is converted back to heat. The energy used to do actual work is used for that. Some of it comes back out as heat
The work also becomes heat in the end.
Directly, as you phrased the question: No.
Indirectly: Yes. Because we would automatically stop burning fuels when we get all our energy from solar. That would decrease the temerature a tiny little bit.
But the temerature of the planet does not really depend on such actions. For example, the indirect effects of CO2 and Ozone in the atmosphere have much more powerful impacts - and still they can only change the temperature at the planet's surface (that's what our lives depend on). The whole of the planet is yet another thing.
Don't forget industrial heat. If we had infinite electricity for free everywhere there would still be fossil fuels burned for industrial heat. We need more technology to finish it like plasma torches.
No need to despair, the technology is being actively developed and a lot of the sub 600 Celsius temps have an electric solution now.
Industrial electric arc furnace temperatures can reach 1,800 °C (3,300 °F)
I was rather surprised to find out there was something like a smelter running on electricity (well industrial scale one). It will be a big deal if solar panels and wind turbines can be made exclusively with electricity from mining to final product.
Things are moving fast! Can't wait for them to figure out clinker for cement.
Don't forget industrial heat
Why? Is it different from "all of mankind's energy"?
I assumed you meant electricity since solar only makes that type of energy efficiently (and sub 100C)
wo:mankind FTFY
but serious answer: no. if humanity sources all its electricity through solar panels, these solar panels would cover <1% (IIRC) of earth's surface area, so the effect would be negligible.
Start reflecting sunlight back into space and increase the earth's albedo
In theory yes, but in practice no. Before we used fossil fuels (say 1000 years ago) the earth was on a slight cooling trend because a little organic matter still gets converted to coal. I can't find the amount, but IIRC it was something like enough for -0.1C every thousand years. That number is so small that even a tiny amount of fuel use would keep us even.
Assuming 25% efficiency, 25% of the sunlight will be converted into electricity. However, once that energy gets used later, most of it will be converted into heat, one way or another. The main way that it will decrease heat being released into the atmosphere is by replacing less efficient methods of energy generation.
For example, it you normally heat a house with a 90% efficient gas burner to generate 900W of heat on average, you are burning enough gas to generate 1000W of heat on average throughout the day. Lets also say the house gets 4000W of heat across its roof on average throughout the day. Thats 5000W of heat being released into the atmosphere total.
Lets now say you convert to solar panels and now get 25% of that energy from the sun converted to electricity, then into heat in the house. Electric heating is essentially 100% efficient, so you get 3000W of sunlight converted directly to heat in the panels, 1000W of electricity which is also turned into heat in the house = 3900W of heat + 100W of extra electricity (turned into heat elsewhere). The 1000W of gas gets eliminated completely.
It probably wont be anywhere near the numbers listed here and batteries will play a huge role in averaging out these numbers due to varying generation and use throughout the day. Additionally this doesnt account for things like cars and othergas based systems which wont / cant be replaced economically, other technologies like radiative cooling paint, and the fact that global temperatures will likely continue to rise due to the continued release of co2 and other gases. It might slightly slow things down though
Converting electricity generation to renewable alone isnt enough to reverse global warming, it would also require converting systens which use gas and other fossil fuels to electric
-
It would decrease temperatures because no energy emissions brings hope that natural carbon sinks can come close to reducing atmospheric CO2 levels. Hydrogen replacing heat in iron/steel and cement could be enough. But it needs to be quick.
-
Solar panels provide shade which can cool the ground/water beneath them. At night, they release heat faster than ground, with less of it absorbed by ground relative to air and upwards to higher atmosphere.
-
google ai does say that more efficient solar panels get less hot. 2-5C over "standard panels", which I cannot source, but would assume its 2C per 5 %point extra efficiency.
Nope, it only helps to not increase it further.
Yes, if the panels were in outer orbit, and mostly powering things outside our planet.
A little simplified energy cannot be destroyed only change form, each time it changes it loses a little bit of energy to heat. Over time that means all energy will become heat.
So the only way to not heat up the earth with energy is to either make sure it doesn't get to earth, or that we let it out.
Orbital solar cells could keep enough light from reaching earth to cool it, but releasing the energy dirtside would mostly cancel that out. So, we cover the earth orbit with panels and use them to fuel space things.
All of this requires more tech, a lot of resources and time to prepare though. And also a feasible way to store and use that energy in space. Maybe we shoot batteries at a moon base or orbital mining operation?
